Newton’s Law of Gravity
Gravity is a universal attractive force acting between all matter.
Doubling the mass of an object doubles the force between the two objects whereas doubling the distance between the two objects makes the force one quarter what it was before (it is an inverse square law).
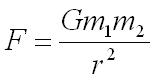
F is the force in newtons (N) between the two objects.
G is the universal gravitational constant = 6.67 x 10-11N m2 kg-2.
m1 and m2 are two masses (measured in kg) whose centres are a distance r apart (measured in m).
Gravitational field strength
The gravitational field strength g is the force per unit mass (measured in N kg-1).
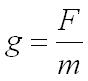
The magnitude of g in a radial field is given by the equation below.
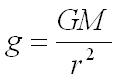
Gravitational potential
The gravitational potential at a point in a field is the potential energy per unit mass (so it’s unit is the J kg-1). It is the work done in bringing a unit mass from infinity to that point. The gravitational potential at an infinite distance is zero. Gravitational potential is a scalar.
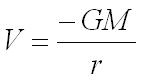
The work done W (measured in joules) in moving a mass m (measured in kilograms) from a point in a field with gravitational potential V1to gravitational potential V2 is given by the equation below.
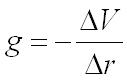
Orbits of planets and satellites



