We are only going to consider three quarks.
- up quark (u)
- down quark (d)
- strange quark (s)
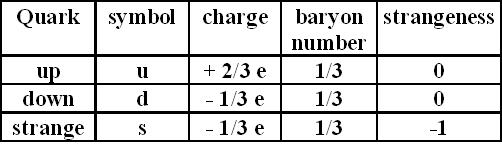
Combinations of quarks form baryons and mesons.
Baryons – always contain 3 quarks. For example a proton contains the quarks, up up down. Whereas an antiproton contains the quarks, antiup antiup antidown.

Mesons – always contain 2 quarks ( a quark and an antiquark). For example the p+meson contains the quarks, up and antidown.
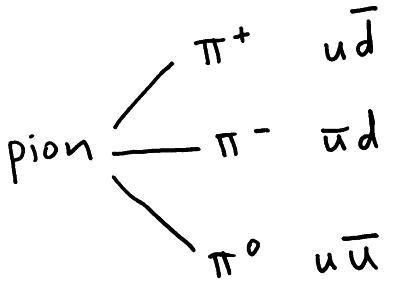
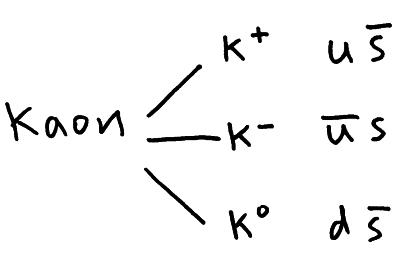
Conservation laws for particle interactions
During particle interactions the following are conserved (the number before the interaction must equal the number after the interaction).
- charge
- baryon number
- lepton number
- strangness
Links to other pages in this topic;



