The resultant force acting on an object can cause objects to accelerate or decelerate.
resultant force = mass x acceleration
(newton, N) (kilogram, kg) (metres per second2, m/s2)
distance-time graphs
The gradient of a distance-time graph represents the speed of the object.
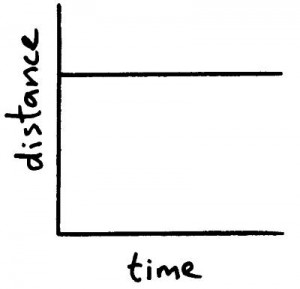
Graph for stationary object.
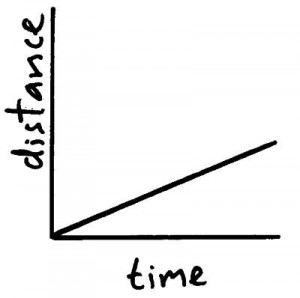
Graph for a slow moving object (small gradient).
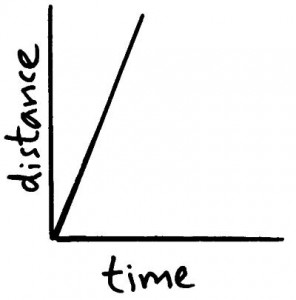
Graph for a fast moving object (steep gradient).
Velocity & Speed
Speed example = 5 m/s
Velocity example = 5 m/s North
A speed only has a size like 20 m/s but a speed in a particular direction like 20 m/s left is called a velocity.
Acceleration
The acceleration of an object is measured in metres/second2 ( m/s2).
acceleration = change in velocity
time taken for change
velocity-time graphs
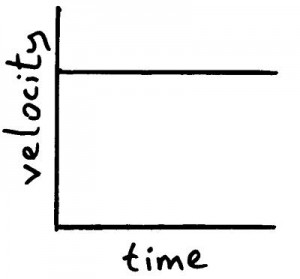
Graph for object moving a constant velocity.
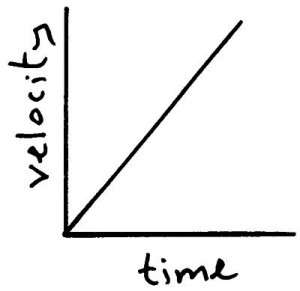
Graph for object accelerating.
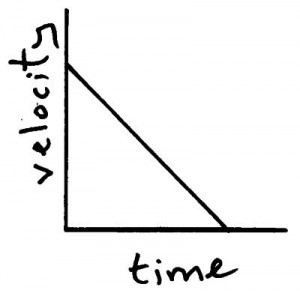
Graph for an object decelerating.
Acceleration for a velocity-time graph
Finding the gradient of a velocity-time graph gives you the acceleration of the object. The greater the gradient the greater the acceleration.
Distance travelled from a velocity-time graph
The distance travelled by an object can be found from the area underneath a velocity-time graph.
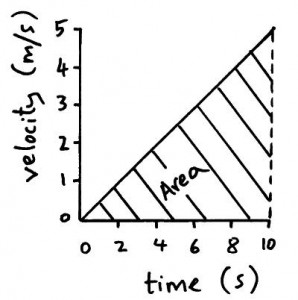
The area underneath this graph is a triangle.
The area of a triangle = 0.5 x base x height = 0.5 x 10 x 5 = 25m.
The distance travelled by the object is 25m.



